On the scientometric value of full-text, beyond abstracts and titles: evidence from the business and economic literature
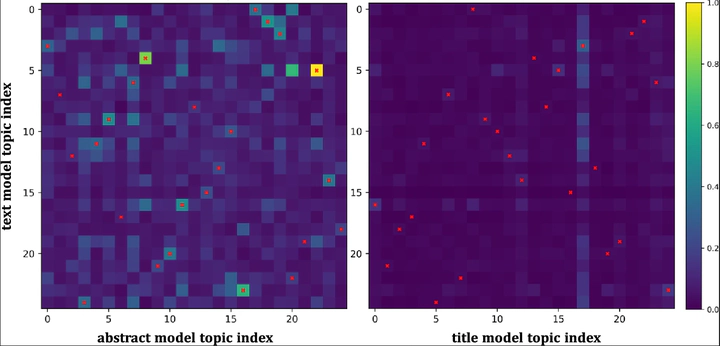 Image credit: Kevin Riehl
Image credit: Kevin RiehlAbstract
Are abstracts or titles a good proxy for what an article contains? The majority of scientometric studies have used easily accessible representations of publications such as reference and author lists, citations, keywords, titles, and abstracts, rather than full-texts. However, better accessibility to full-text databases is on the rise. First studies employing full-texts are promising, yet the extent to which scientometric exploration of papers beyond title and abstract is beneficial to gain further insights is still under discussion. In this paper, we analyse the similarity between a paper’s title, abstract and full-text and examine whether scientometric analyses should better rely on full-texts. Our dataset includes 66,392 articles published in 27 leading journals in the business administration and economics literature. We examine the use of these representations in textual analysis, topic modelling and research evaluation. The results suggest that, unlike titles, abstracts and full-texts exhibit significant similarities and can be used interchangeably. While, abstracts contain less extraneous information and approximately 30% less noise compared to full-texts in topic modelling, full-text-based models to explain future number of citations yield a 5% higher explanatory power. Additionally, we recommend considering the influence of diverse writing styles as a textual and rhetorical property, as our analysis demonstrates its significant explanatory power for future publication success.